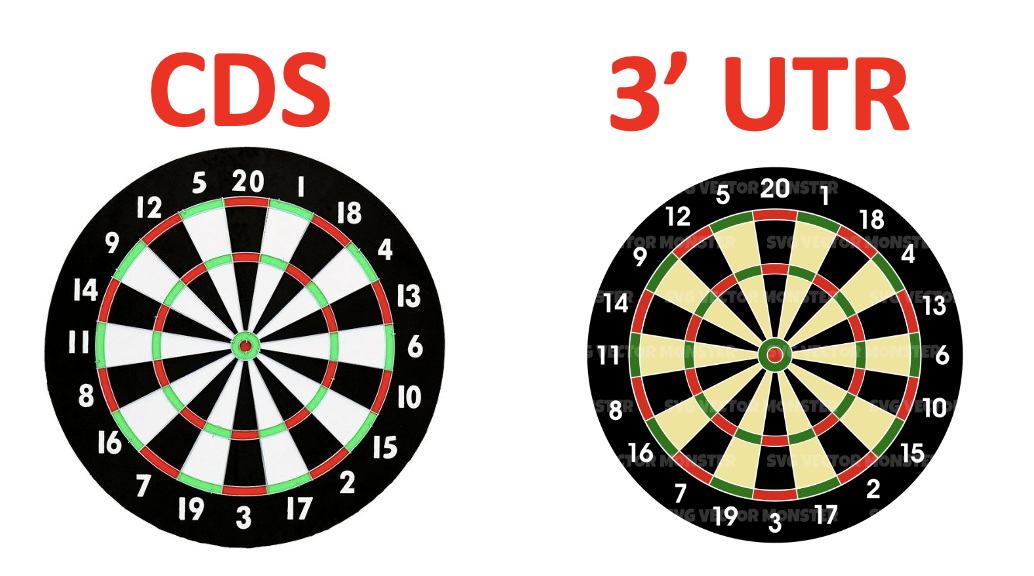
A Brief Interview with Patrick Hörner on Malaria and insecticide resistance
Malaria, a devastating disease that has plagued humanity for centuries, continues to take a heavy toll on vulnerable populations worldwide. Caused by the Plasmodium parasite, this disease is primarily transmitted through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitos. Malaria exacts a staggering toll, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where it remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Its symptoms, which range from high fevers to severe anemia, can incapacitate individuals and, if left untreated, can be fatal. One of the Read More






